The salary of an employee comprises both Fixed and Variable pay. Paybooks helps the employer in creating and editing various Salary components in simple and easy-to-understand steps.
To create a salary component
Go to Settings >> ‘Salary Components’
Click on ‘New’.
Update the following details:
Name: Enter the name of the Salary Component
Abbreviation: Enter the short name of the component. Example: “CONV” for Conveyance, “MEDAL” for Medical Allowance, etc…
Note: There shouldn’t be any space or special character
It should be one word containing 7 characters.
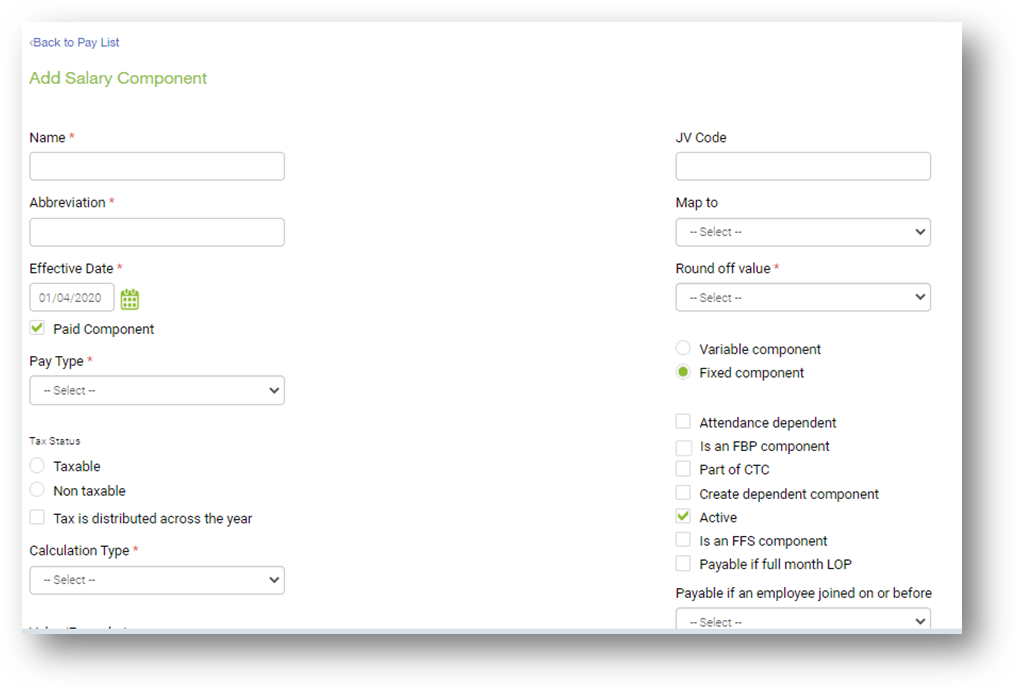
- Effective Date: By default, the effective date will be considered as 1st April.
You have the option to change the date if the component is created during the year.
This is required to know the effective date of the component.
- Paid Component: Check the box if the Component is part of the employee's Salary and needs to be displayed in the payslip.
The box can be unchecked:
- When creating statutory components like PF, ESIC, etc or
- Components paid outside payroll or
- Components that are part of CTC but not to be paid like Performance Bonus, Commission, etc
- Pay Type: There are 5 options of pay types that can be selected from the drop-down.
- Earnings: All income like Basic, HRA, Conveyance, etc., are earning components. They can be fixed or variable in nature.
- Deductions: All recoveries which are not statutory in nature like Salary Advance, Loans, etc
- Reimbursement: Reimbursement refers to the monetary compensation paid by a company to its employees for incurring expenses out of their pocket for official purposes. Eg Boarding, Lodging, Local Conveyance, etc.
- Overtime: Amount that is paid for work done beyond working hours. Eg if the employee works more than 40 hours a week (considering 8 hours per day for 5 working days), then the employee will be eligible to receive Overtime for the excess hours.
- Statutory Component: Statutory component is a mandatory deduction deducted from the employee’s salary under various statutes.eg Provident Fund, Professional Tax, Income Tax, etc.
- Taxable: Check this box if the component needs to be considered for tax calculation.
- Non-Taxable: Check this box if the component has no tax implication like all reimbursement components.
- Tax is Distributed across Year: Check this box only if the component has been checked as taxable and tax deduction needs to be distributed across the Financial Year.
- Round-off Values: Select from the Drop-down list to round off the salary component as per your Company policy.
- Calculation Type: There are 2 types of Calculations i.e., Flat and Formula based
- Flat: Select this option if the component is not formula based and should be entered manually / open-ended while employee creation or salary changes. Then enter “0” in the formula box.
- Formula: Select this option if the component is formula based.
Click on the Formula button to write a formula.
Define the formula by selecting an appropriate function (from Brackets, abbreviations & Operators). The formula can be derived using only abbreviations available in the formula bar.
Click on Add and then click on Validate.
If the formula defined is correct, a message will be displayed - “Valid Expression”.
If the formula defined is incorrect, a message will be displayed - “Invalid Expression”.
Try to redefine the formula and validate it until the message is displayed as “Valid Expression”.
Click on Save.
- Sample Formula Syntax: If(A>B; A*40%; A*50%)
- Components like: Professional Tax and Income Tax are pre-configured in the system and are slab based as per prevailing statutory rules.
- Calculated On: If the Calculation Type is selected as Formula, then you will get these two options.
Deducted Amount: The system will consider the ‘Prorated Amount’ based on the attendance
Actual Amount: The system will consider the ‘Fixed Amount’ as per the Salary Structure.
JV Code: To pass salary entries into your financial accounting software, you need to update the JV code as per your chart of accounts. A ledger report will be generated based on the updated JV code.
Map To: There are pre-configured rules that are set in the system. You need to map the created components to apply the respective configurations.
Example: HRA must be mapped to IT HRA. As per this mapping, HRA exemption shall be calculated.
Another example is VPF Component, which should be mapped to VPF, this will reflect in the PF Report and calculate exemption under 80C.
Variable Component: Select this option if the salary component is not fixed and varies monthly. Example Bonus, Incentives, Overtime, etc.
Fixed Component: Select this option if the salary component is fixed and does not change monthly. Example: Basic, HRA, Conveyance, etc.,
Is an FBP component: Enable this option if you have opted for the Flexible Benefit Plan and would want the component to be part of FBP
Attendance Dependent: Check the box if this component needs to be paid based on attendance.
Note: If Attendance Dependent is enabled then select “Calculated on” as “deducted amount”.
Part of CTC: Check the box if you want this component to be part of the CTC
Create Dependent Component: Check this box so that the arrears /recoveries component will be created separately. This is applicable if the component is fixed in nature.
Is Active: If the “Active” box is checked, the component will reflect in the pay register and all the reports.
If unchecked the created component will not reflect in the Pay Register and other reports even though it is created.
Overtime: If you have selected the Pay type as Overtime, then you need to configure the Days or Hours and enter the maximum OT unit, as per company policy.
Note:
Click on ‘ADD’ to create the component.
Once the component is created, it should be assigned to the employees so that this becomes part of their salary.
Go to Employees > Payroll Settings > Salary Components
Click on Pay Allocation

To know more about allocating salary components, please read How to allocate a pay component in the salary structure of employees?
